Introduction
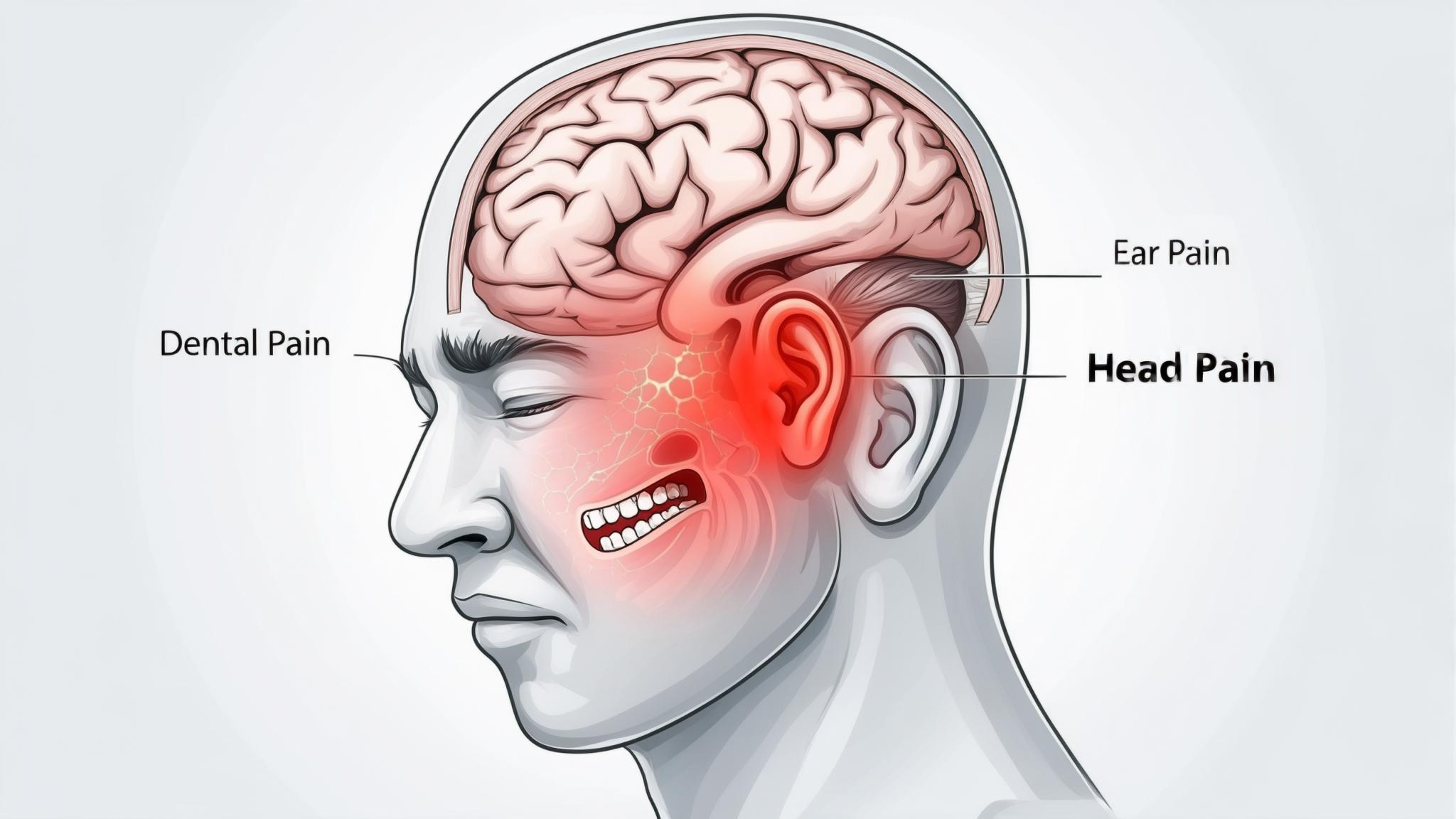
Have you ever experienced a toothache that seemed to resonate through your entire head or even caused discomfort in your ear? This phenomenon is known as referred pain, where pain in one part of your body affects another seemingly unrelated area. Understanding this connection is crucial because it can help you address the root cause of your discomfort more effectively.
In this article, we'll delve into the concept of referred pain, explore how dental issues can lead to ear or head pain, and provide guidance on when to seek professional help.
Understanding Referred Pain
What is Referred Pain?
Referred pain occurs when pain in one part of the body is perceived in another area. This happens due to the complex network of nerves that transmit pain signals throughout our bodies. For instance, a heart attack might cause pain in the arm rather than the chest. Similarly, dental pain can manifest in the ear or head.
Anatomy of Dental Pain
The nerves responsible for sensation in the teeth and gums are closely linked with those in the head and neck. This intricate network can cause pain signals from a toothache to be misinterpreted by the brain as coming from the ear or head instead.
Sources of Dental Pain
Common Dental Issues
Several dental problems can lead to pain that might be referred to the ear or head:
- Tooth Decay: Cavities can cause significant discomfort and are a common source of dental pain.
- Gum Disease: Infections or inflammation of the gums can lead to pain that spreads beyond the mouth.
- Tooth Abscess: A pocket of pus caused by infection can result in severe pain.
- Cracked or Fractured Teeth: Damage to a tooth can lead to sharp pain that may be felt in other areas.
Impact on Surrounding Structures
Dental infections and inflammation can affect nearby tissues, leading to pain in the ear or head. This happens because the nerves and blood vessels in these areas are interconnected.
Connection Between Dental Pain and Ear Pain
Anatomy of the Head and Neck
The trigeminal nerve is a major player in this connection. It supplies sensation to the face, including the teeth and gums, and has branches that are close to the ear. When dental pain occurs, it can stimulate this nerve, leading to ear discomfort.
Symptoms Indicating Dental Pain May Affect the Ear
- Pain Localization: Pain that worsens when chewing or in response to temperature changes might indicate a dental origin.
- Accompanying Symptoms: Tinnitus (ringing in the ears) or a sensation of fullness in the ear can accompany dental pain.
Connection Between Dental Pain and Head Pain
Types of Headaches
Dental issues can contribute to different types of headaches:
- Tension Headaches: Often caused by jaw clenching or teeth grinding.
- Migraines: Can be triggered by stress or pain from dental problems.
- Cluster Headaches: Though less common, they can be linked to dental issues.
Mechanism of Headache Development
When dental pain stimulates the nerves in the head, it can lead to headaches. This is because the brain may interpret the pain signals as originating from the head rather than the teeth.
Symptoms Indicating Dental Pain May Affect the Head
- Chronic Headaches: Persistent headaches that don't respond to typical treatments may have a dental origin.
- Jaw Pain: Pain that radiates from the jaw to other areas of the head.
Diagnosis of Referred Pain
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Accurately diagnosing referred pain is essential for effective treatment. Misdiagnosis can lead to unnecessary treatments and prolonged discomfort.
Diagnostic Tools and Methods
- Patient History and Symptom Assessment: Understanding the patient's symptoms and history is crucial.
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination can help identify the source of pain.
- Imaging Techniques: X-rays or CT scans can reveal underlying dental issues.
Treatment Options
Addressing the Source of Dental Pain
Treating the underlying dental issue is key to resolving referred pain. This might include:
- Dental Treatments: Such as fillings, root canals, or extractions.
Managing Referred Pain
- Pain Relief Medications: Over-the-counter or prescription medications can help.
- Physical Therapy and Alternative Treatments: Techniques like massage or acupuncture can provide relief.
Importance of Consulting Healthcare Professionals
Always seek advice from dental or medical professionals to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
When to Seek Emergency Care
Signs of Serious Dental Issues
Seek immediate care if you experience:
- Severe, persistent pain
- Swelling in the face or jaw
- Fever or chills
Differentiating Between Dental and Other Medical Emergencies
Understanding whether your pain is dental or related to another medical issue is vital. When in doubt, consult a healthcare provider.
Recommended Actions
In cases of severe pain, contact your dentist or visit an emergency room for evaluation and treatment.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs of referred pain can lead to timely and effective treatment. Don't hesitate to seek dental care if you suspect your ear or head pain is related to a dental issue. Remember, maintaining good oral health is not only crucial for your smile but also for your overall well-being.